Demystifying Construction Project Scope Complexity with WBS

From cost estimating to project scheduling, and other project control discussions.
Demystifying project scope complexity with WBS. Project scope complexity can be considered within the context of work tasks, which center around different types of resources used, the varying environment under which work is completed, the level of technical know-how required, and the interconnectedness of the physical components (elements) that make up the project.
As such, a small or mega project can be seen as complex if it involves varying resources. It is constructed in a varying environment, requires intricate know-how and technologies, and has mostly interconnected components. All of which translates to increasing factors, conditions, and variables to consider.
How does one view projects like these without getting overwhelmed by their complexity? Simply put – break them down into chunks. This is where the WBS comes into play.
WBS stands for work breakdown structure. Breaking the work down into chunks for planning, cost estimating, project scheduling, and other purposes.
Developing a WBS should align with the schedule of bid/pay items (bid schedule) and the work tasks as used in developing the cost estimates, project schedules, and others.
It all starts from looking at each bid/pay item and identifying one or a combination of ways to group them so as to easily differentiate them and communicate the project scope for various purposes.
Here is a combination of ways to group a project scope of work into chunks so as to easily differentiate them and communicate the project scope for various purposes.
- By Facility Type (Feature of Work)
- By Systems
- By Type of Work (group of related items of work)
- By Location
- By Phase and/or Stage
- By Segments
- By Discipline
- By Functional Components (Elements)
- By Size and Shapes
- By Construction Materials
- By Crew/Construction Method
- By the Responsible Party
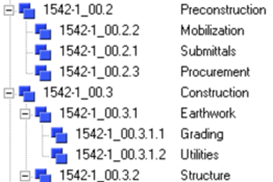
Here is the most basic structure of a WBS – a systematic method that is used in construction to break the scope of work into chunks.
Org Chart Format.
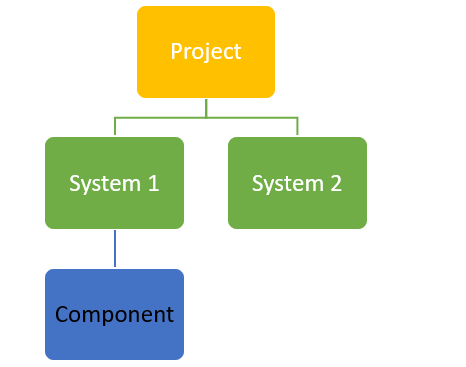
Outline Format.